- Home
- Jacketted Hose Assemblies
- Home
- Products
- Industries
- Company
- Contact Us
- Home
- Products
- Industries
- Company
- Contact Us

| Core & Jacket | : | SS304/304L/316/316L/321 |
| Braid Material | : | SS304/304L/316/316L |
| Operating Temperature | : | 400°C max. (600° C is possible as a special design). |
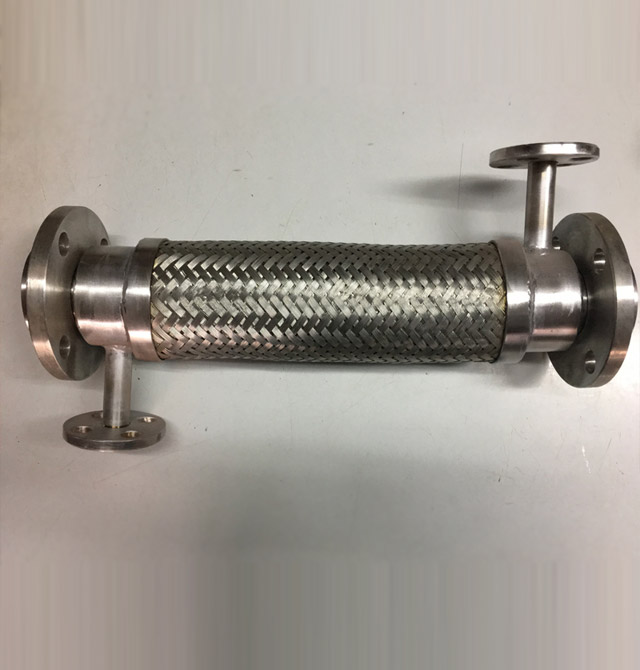


APPLICATIONS : This type of assemblies is used when ordinary insulation is not sufficient for certain applications or when specific minimum temperatures are required to convey viscous substances.
It consists of two hoses one inside the other, with various cross sectional differences. One of the hoses, generally the external one carries a heating or cooling agent. Sometimes it is the other way round. In other cases, the external hoses is used as a safeguard.